Medicine & Gastroenterology
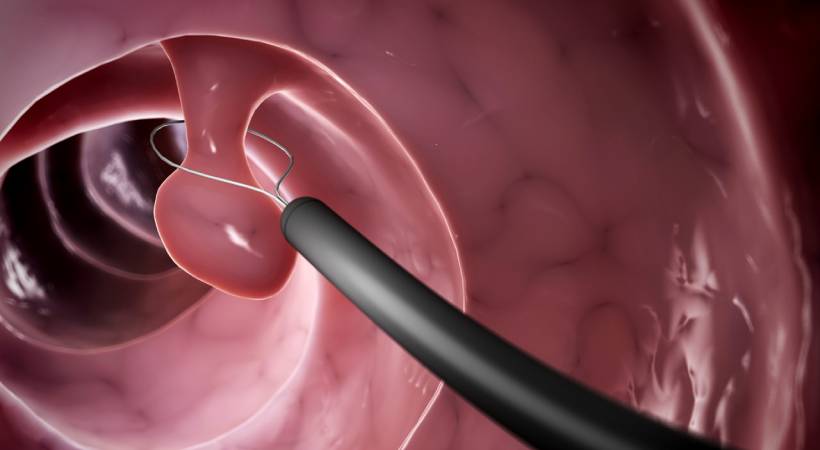
Overview:
Polypectomy is a therapeutic procedure performed during colonoscopy to remove colorectal polyps. Colorectal polyps are abnormal growths in the lining of the colon or rectum, and while most are non-cancerous, some can progress to colorectal cancer over time.
Symptoms:
Polypectomy is indicated when individuals undergo colonoscopy, and polyps are detected. Colorectal polyps are often asymptomatic, and their presence is typically identified during routine screenings or in response to symptoms such as changes in bowel habits or rectal bleeding.
Causes:
Colorectal polyps may develop due to genetic factors, age, or lifestyle choices such as a high-fat, low-fiber diet. While most polyps are benign, some may carry the risk of progressing to colorectal cancer, making their removal crucial.
Prevention:
Preventive measures involving polypectomy revolve around regular colorectal cancer screening, especially for individuals over the age of 50 or those with a family history of colorectal cancer. The removal of polyps during colonoscopy is a preventive measure aimed at reducing the risk of colorectal cancer development.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, polypectomy is a preventive and therapeutic procedure that plays a significant role in reducing the risk of colorectal cancer. By identifying and removing polyps during colonoscopy, healthcare professionals contribute to the early detection and management of potential precursors to colorectal cancer. Regular screenings and polypectomy procedures are integral components of colorectal health maintenance.
