Medicine & Gastroenterology
Overview:
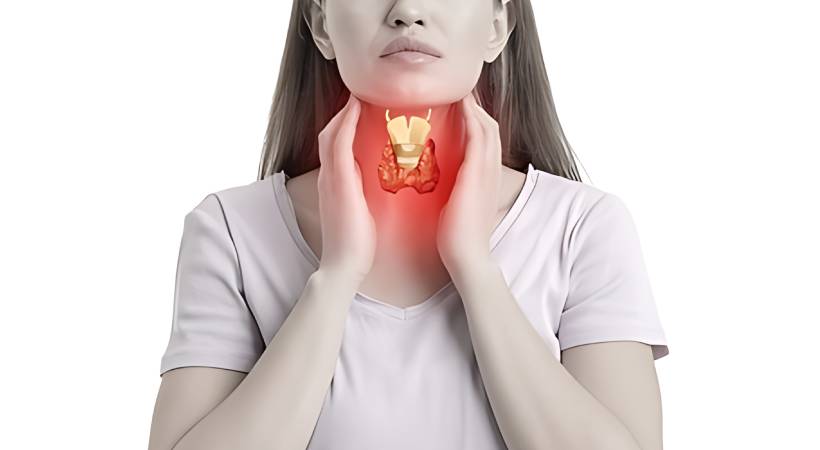
The thyroid, a small butterfly-shaped gland in the neck, plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism and energy levels. Thyroid diseases encompass conditions such as hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) and hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid), both of which can have widespread effects on the body.
Symptoms:
Hypothyroidism symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, and sensitivity to cold. Hyperthyroidism symptoms may involve weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and nervousness. Both conditions can affect mood, energy levels, and overall well-being.
Causes:
Hypothyroidism can result from autoimmune disorders, radiation therapy, or certain medications. Hyperthyroidism may be caused by autoimmune conditions like Graves’ disease or thyroid nodules that produce excess thyroid hormone.
Prevention:
Preventing thyroid diseases involves maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing stress, and avoiding excessive iodine intake. Regular thyroid function tests can help identify any abnormalities early on, allowing for timely intervention.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, thyroid diseases highlight the importance of thyroid function in maintaining overall health. Regular monitoring, lifestyle adjustments, and prompt medical attention are essential for managing these conditions effectively. By addressing thyroid health, individuals can optimize their metabolism and ensure a balanced and energized life.
